EDWIN LOCKE’S GOAL-SETTING
THEORY
v This
motivation theory was developed primarily by Edwin Locke and Gary Latham (1990).
v A
powerful way of motivating people.
v Essentially
linked to task performance.
v Employees
are motivated by clear goals and appropriate feedback.
v Spcific
and challenging goals along with appropriate feedback contribute better task
performance.
Some
Key Concepts
1. Goal
:
·
“Something that the person wants to
achieve,” (Locke & Lathan-1990)
2. Formation
of Goals:
·
Long term goals- A long-term
goal is something you want to do further in the future. Long-term goals require
time and planning. Here are examples of goals that can take several years to
achieve:
Ø Graduate from college
Ø Save for retirement
Ø Have my own business
·
Short term Goals-
A short-term goal is something you want to do in the near future. The near
future can mean today, this week, this month, or even this year. A short-term
goal is something you want to accomplish soon. Examples include:
Ø Take
a class
Ø Buy
a new television
Ø Write
my resume
3. Goal
Setting:
·
“A specific outcome that an individual
is striving to achieve.” (Alderman-1999)
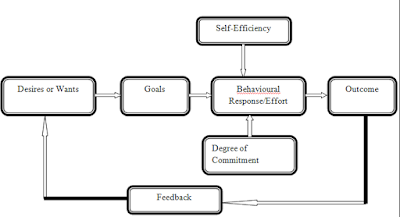
How does Goal Setting Motivate ?
Goal:
·
Direct attention
·
Regular effort
·
Increase persistent
·
Encourage development of strategies and
action plans
In his 1968 article “Toward
a theory of Task Motivation and Incentives”, Locke’s research
should that
·
There is a relationship between
difficult and specific goals with people’s performance.
·
Specific and difficult goals lead to
better task performance than vague or easy goals.
E.g. telling someone to ‘Try hard’
or ’Do best’ is less effective than ‘Try to get more than 80% correct.’
Source:Adopted from E.A. Locke and G.P.
Lathan.A theory of ‘Goal Setting’ and ‘Task Performance’ (Englewood Clifts by
permission of Edwin Locke.
Goals should be SMART
Five Principles
of Goal-Setting
Dr. Edwin Locke
and Dr. Gary Lathan- “A Theory of Goal Setting and Task
performance.”-1990
To motivate
Employees, Goals must have:
v Clarity
v Challenge
v Commitment
v Feedback
v Task complexity
Ø
Specific,clear,unambiguous
and measurable goals leads to greater output and better performance.
Ø
Goals
should be realistic and chaalengable.
Ø
This
gives an employee feeling of pride after attaining it and sets him up for
ttainment of next goals.
Note:
·
An
appropriate balance should be created between a challenging goal and realistic
goal.
·
Goals
should be chievable.
Ø Employees’
participation in setting goal makes goal more acceptable, and
Ø Leads to more
involvement.
Ø Provides
opportunities to clarify expectations,adjust goal difficulty and gain
recognition.
Ø Helps employees
to work with more involvement.
Ø Leads to greater
job satisfaction.
Ø For high complex
goals /assignments , special care should be taken to ensure the work doesn’t
become to overheming.
Goal setting Theory: Certain
eventualities
Again Goal attainment is
dependent on several factors
Goals should be-
Ø Open,known and
broadcasted.
Ø Set up by
individual rather than designated.
Ø Consistent with
organizational goals and vision.
Advantages
Goal Setting-
Ø Is
a technique used to raise incentives for employees to complete work quickly and
effectively.
Ø Leads
to better performance by increasing motivation and efforts but also through
improving feedback quality.
Limitations
Ø At
times the organizational goals are in conflict with the managerial goals.Goal
conflict has a determinant effect on the performance.
Ø Very
difficult and complex goals stimulate riskier behaviour.
Ø There
is no evidence to provide that Goal-Setting improves job satisfaction.
Ø If
the employee lacks skills and competencies to perform actions essntial for
goals than the goal-setting can fail and lead to undermining of performance.
Implicationsfor
Educational Management
Education management
should-
Ø Give
employees sufficient time to meet the goal.
Ø Give
employees sufficient time to practice/learn what is required for them.
Ø Make
sure that the conditions surrounding the goal don’t inhibit people from
accomplishing their objectives.
Ø Provide
feedback on goal performance.
Ø Recognise
all the employees for their good performance.
Implications for
Employees
Ø Goal
setting is necessary for employees’ success.
Ø Employees
must use clear,challenging goals and commit themselves to achieving them.
Ø Employees
must take into consideration the complexity of the task.
In Brief
Goals indicate and give
direction to an employee about
Ø What
needs to be done ,
Ø How
much efforts are required to be put in.





No comments:
Post a Comment